
Top 50 Interview Questions For Digital Marketing
Do you feel uncomfortable while facing interview questions for digital marketing? If yes, then this article can prove to be a game changer for you. It will be easy for you to crack any interview on digital marketing if your basics and preparation for the interview is great.
Digital marketing questions and answers will become easy for you if you know the details of the concept. Now, there are some core concepts that you need to address while handling digital marketing interviews.
All these questions are designed to assess technical knowledge, strategic thinking, and practical experience, suitable for roles from entry-level to senior positions.Digital marketing interview questions and answers can help you to meet your needs.
Table of Contents
- List Of Interview Questions For Digital Marketing
- 1. What Is Digital Marketing?
- 2.What Do You Know About On Page Optimization & Off Page Optimization?
- 3. Discuss About Different Types Of Search Engine Optimization Techniques?
- 4. What Do You Know About Responsive Web Design?
- 5. Explain The Importance Of Social Media In Digital Marketing?
- 6. Explain The Importance Of Content Marketing In Digital Marketing?
- 7. How Useful Is AMP In Digital Marketing?
- 8. What Do You Know About Conversion Optimization?
- 9. Explain The Difference Between Adwords & Adsense?
- 10. Explain The Importance Of Backlinks In SEO?
- 11. What Do You Know About Automated Bidding Strategies?
- 12. Differentiate Between Direct Marketing & Branding?
- 13. What Are The Disadvantages Of Digital Marketing
- 14. What Are The Advantages Of Digital Marketing?
- 15. What Are The Trends Of Digital Marketing This Year?
- 16. What Are The Popular Digital Marketing Tools?
- 17. How To Categorize Digital Marketing?
- 18. What Are The 4 C’s Of Digital Marketing?
- 19. Differentiate Between Do Follow And No Follow Links?
- 20. What Is A 301 Redirect?
- 21. What Are The Best Practices To Rank YouTube Channels?
- 22. What Is Mobile First Indexing?
- 23. List The Most Popular Local SEO Ranking Factors?
- 24. How To Avoid Content Penalty For Duplicates?
- 25. What Are The Ways You Can Increase Web Page Speed?
- 26. When Should Short Tail And Long Tail Keywords Be Targeted?
- 27. What Are The Most Effective Ways To Increase Traffic On Your Website?
- 28. What Are The On-Page & Off-Page Optimization?
- 29. What Is AMP?
- 30. What Is The Use Of Anchor Tags In SEO?
- 31. Explain The Significance Of CTR?
- 32. What Can You Do To Improve The Conversion Rate?
- 33. Explain What Google Adwords Is?
- 34. Can You Tell Us About Few Google Adwords And Few Google Ad Extensions Name?
- 35. How Google Ad Ranks?
- 36. What Is Ad Scheduling?
- 37. What Are The Different Ad Formats Available On Google Ads?
- 38. What Is RSLA And How It Works?
- 39. What Types Of Audiences Can Be Used In GDN?
- 40. What Are The Types Of Keywords Matching Available In Google Ads?
- 41. What Are Some Reasons As To Why Ads Could Be Rejected?
- 42. What Are The Different Kinds Of Bidding Available?
- 43. What Are Some Automatic Bidding Strategies?
- 44. What Is The Quality Score In Google Ads?
- 45. What Are The Hallmarks Of A Good PPC Landing Page?
- 46. What Is The Difference Between Hard And Soft Bounce Emails?
- 47. How Do You Improve The Click Through Rate Of Your Email?
- 48. Define The Following Metrics:- Open Rate, Click Through Rate, Response Rate, and Forward Rate?
- 49. How To Recapture Inactive Customers?
- 50. What Are The Different Ways To Segment Buyer Personas?
List Of Interview Questions For Digital Marketing
There are several interview questions for digital marketing that you must be well aware off. Some of the key aspects that you must focus from your end are as follows:-
1. What Is Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing is the promotion of products, services, or brands through digital channels like search engines, social media, email, websites, and mobile apps. Unlike traditional marketing (e.g., TV, print), it leverages online platforms to reach targeted audiences with measurable, data-driven strategies.
Key components include SEO, PPC, content marketing, social media marketing, and email campaigns, all aimed at engaging users, driving traffic, and achieving business goals like conversions or brand awareness. Its strength lies in precise targeting, real-time analytics, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods.
2.What Do You Know About On Page Optimization & Off Page Optimization?
It is one of the crucial interview questions for digital marketing that you need to be well aware of before the interview. So, let’s explore the facts in this regard.
On-Page Optimization
On-page optimization refers to all SEO activities performed directly on the website to improve its search engine rankings. These efforts focus on optimizing content and technical elements within the site’s control.
- Key Elements:
- Content Quality: Creating high-quality, relevant, and engaging content that aligns with user intent and incorporates target keywords naturally.
- Keyword Optimization: Strategically placing keywords in titles, headings (H1, H2), meta descriptions, URL structures, and body content.
- Meta Tags: Writing compelling meta titles and descriptions to improve click-through rates (CTR) and describe page content accurately.
- Internal Linking: Adding links to other pages on the same website to improve navigation and distribute link equity.
- Purpose: To make the website search-engine-friendly, improve relevance for target keywords, and enhance user satisfaction, which directly impacts rankings.
- Example Tools: Google Keyword Planner, Yoast SEO, Screaming Frog.
Off-Page Optimization
Off-page optimization involves activities outside the website to boost its authority, credibility, and visibility in search engines. It primarily focuses on building the site’s reputation through external signals. It is a crucial interview questions for digital marketing.
- Key Elements:
- Backlinks: Acquiring high-quality, relevant links from authoritative websites, as they signal trust and credibility to search engines.
- Social Media Engagement: Promoting content on social platforms to increase brand visibility and drive traffic, indirectly supporting SEO.
- Guest Blogging: Publishing content on reputable sites with a link back to your website to build authority and referral traffic.
- Purpose: To build the website’s authority and trustworthiness in the eyes of search engines, which improves rankings and drives referral traffic.
- Example Tools: Ahrefs, Moz, SEMrush for backlink analysis; BuzzSumo for influencer outreach.
Level Up Your Skills. Make Your Mark in the Digital Marketing Industry.Learn Practical Skills Directly from Industry Professionals |
|
| Advanced Digital Marketing | |
| More Learning Options for you: Google Ads Certification | Diploma in Digital Marketing | Facebook Ads Course |
3. Discuss About Different Types Of Search Engine Optimization Techniques?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) techniques are strategies and practices used to improve a website’s visibility and ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). These techniques can be broadly categorized into several types based on their focus and approach. Below is a detailed discussion of the different types of SEO techniques, organized for clarity:
1. On-Page SEO Techniques
On-page SEO involves elements of optimization directly on the website to improve its relevance and user experience for search engines and visitors. It is a crucial interview questions for digital marketing.
- Keyword Optimization
- Content Optimization
- Meta Tags
- Internal Linking
- Technical On-Page SEO
2. Off-Page SEO Techniques
Off-page SEO focuses on building a website’s authority and reputation through external activities, primarily outside the website’s control.
- Link Building:
- Social Media Marketing:
- Brand Mentions and Citations:
- Influencer Outreach:
- Online Reputation Management:
3. Technical SEO Techniques
Technical SEO focuses on optimizing the website’s infrastructure to ensure search engines can crawl, index, and rank it effectively. It is also a crucial interview questions for digital marketing to take care of.
- Site Speed Optimization
- Mobile Optimization
- Crawlability and Indexability
- Schema Markup
- HTTPS and Security
4. Local SEO Techniques
Local SEO targets geographically specific audiences to drive traffic to physical businesses or location-based services. It is one of the important questions for digital marketing to look into. Interview questions for digital marketing can make things work well in your way.
- Google My Business (GMB) Optimization
- Local Citations
- Localized Content
- Local Backlinks
5. Content SEO Techniques
Content SEO focuses on creating and optimizing content to rank higher and engage users effectively. Interview questions for digital marketing encircles this question as well.
- Content Creation
- Content Promotion
- Keyword Mapping
- User Intent Optimization
4. What Do You Know About Responsive Web Design?
Responsive Web Design (RWD) is an approach to web design that ensures a website adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes, devices, and orientations, providing an optimal user experience across desktops, tablets, smartphones, and other devices. It’s a critical component of modern digital marketing and SEO, as it enhances user satisfaction, improves accessibility, and aligns with search engine priorities like Google’s mobile-first indexing. It is one of the crucial interview questions for digital marketing.
5. Explain The Importance Of Social Media In Digital Marketing?
Social media plays a pivotal role in digital marketing by providing platforms to connect with audiences, build brand awareness, drive engagement, and achieve business goals. Its importance stems from its ability to reach vast, targeted audiences in real-time, offering measurable results and cost-effective strategies. Below is a concise explanation of why social media is critical in digital marketing:
1. Enhances Brand Awareness
- Reach: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, and TikTok have billions of active users, allowing brands to reach diverse audiences globally or locally.
- Visibility: Regular posting, sharing, and paid ads expose brands to new audiences, increasing recognition and recall.
- Viral Potential: Engaging content (e.g., videos, memes) can go viral, amplifying brand exposure organically.
2. Facilitates Audience Engagement
- Two-Way Communication: Social media enables direct interaction with customers through comments, messages, and polls, fostering relationships and trust.
- Personalization: Brands can tailor content to specific demographics, interests, or behaviors, making interactions more relevant.
- Community Building: Groups, hashtags, and branded content create loyal communities around brands, encouraging advocacy.
3. Drives Website Traffic and Conversions
- Referral Traffic: Links in posts, stories, or ads direct users to websites, landing pages, or e-commerce stores.
- Call-to-Actions (CTAs): Social media ads and posts with strong CTAs (e.g., “Shop Now,” “Learn More”) drive conversions like sales, sign-ups, or downloads.
- Retargeting: Platforms like Facebook Ads allow retargeting of website visitors, increasing conversion rates.
4. Supports Targeted Advertising
- Precise Targeting: Social media platforms offer advanced targeting options based on demographics, interests, behaviors, and location, ensuring ads reach the right audience.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Paid campaigns (e.g., Instagram Ads, LinkedIn Sponsored Posts) allow budget flexibility, with options like CPC or CPM to optimize ROI.
- Analytics: Built-in tools (e.g., Facebook Insights, Twitter Analytics) provide real-time data on ad performance, enabling quick optimization.
6. Explain The Importance Of Content Marketing In Digital Marketing?
Content marketing is a strategic approach within digital marketing that focuses on creating, distributing, and promoting valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract, engage, and retain a target audience. It plays a critical role in building brand authority, driving traffic, and achieving business goals. This is one of the crucial interview questions for digital marketing that you must be well aware of.
1. Builds Brand Awareness and Visibility
- Reach: High-quality content (blogs, videos, infographics) shared across websites, social media, or email exposes brands to wider audiences.
- Search Visibility: Optimized content ranks higher on search engines (via SEO), increasing organic discoverability.
- Shareability: Engaging content is more likely to be shared, amplifying brand reach organically.
2. Establishes Authority and Trust
- Expertise: In-depth content (e.g., guides, whitepapers) showcases industry knowledge, positioning the brand as a thought leader.
- Trust: Providing valuable, accurate content builds credibility, fostering trust with audiences.
- E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness): Content aligned with Google’s E-A-T guidelines enhances SEO performance and user confidence.
3. Drives Audience Engagement
- Relevance: Content tailored to audience needs (e.g., how-to articles, case studies) encourages interaction and deeper connections.
- Storytelling: Compelling narratives create emotional bonds, making brands memorable.
- Interactivity: Formats like quizzes, polls, or videos boost engagement and time spent on the brand’s platforms. You will also get insights about digital marketing executive job description from this article.
4. Supports SEO and Organic Traffic
- Keyword Optimization: Content incorporating target keywords improves search engine rankings, driving organic traffic.
- Backlinks: High-quality content attracts backlinks from authoritative sites, boosting SEO authority.
- Freshness: Regularly updated content signals relevance to search engines, maintaining or improving rankings.
5. Fuels Lead Generation and Conversions
- Lead Magnets: Offerings like eBooks, webinars, or templates capture leads by providing value in exchange for contact information.
- Customer Journey: Content tailored to each stage (awareness, consideration, decision) guides prospects toward conversions.
- CTAs: Strategic calls-to-action in content (e.g., “Download Now,” “Shop Here”) drive actions like purchases or sign-ups. It is another crucial questions for digital marketing.
7. How Useful Is AMP In Digital Marketing?
AMP is a stripped-down version of HTML combined with AMP JS and caching mechanisms (e.g., Google AMP Cache) to optimize page performance on mobile devices. It prioritizes speed by limiting complex elements like heavy JavaScript, ensuring rapid load times, especially for content-heavy pages like articles, blogs, or news.
Importance Of AMP In Digital Marketing
AMP can be a valuable tool in digital marketing, particularly for specific use cases, but its impact varies based on strategy and audience needs. Here’s how it contributes:
1. Improves Mobile User Experience
- Faster Load Times: AMP pages load in under a second, reducing bounce rates and keeping users engaged, especially on slower mobile networks.
- Simplified Design: AMP’s lightweight structure ensures clean, user-friendly layouts, enhancing readability and navigation.
- Impact: Better UX increases dwell time and engagement, key metrics for digital marketing success.
2. Boosts SEO and Visibility
- Mobile-First Indexing: Since Google prioritizes mobile-friendly sites, AMP’s fast-loading pages align with Core Web Vitals (e.g., Largest Contentful Paint), potentially improving rankings.
- Featured Placements: AMP pages may appear in Google’s Top Stories carousel or other rich results, increasing visibility for publishers (e.g., news sites).
- Impact: Higher rankings and featured snippets drive organic traffic, a cornerstone of digital marketing.
3. Enhances Paid Campaign Performance
- Ad Quality: Fast-loading AMP landing pages improve user experience, potentially increasing Google Ads Quality Scores, which lowers cost-per-click (CPC) and boosts ad rankings.
- Conversion Rates: Quick load times reduce drop-offs, improving conversions for PPC campaigns or e-commerce.
- Impact: AMP supports paid advertising by optimizing landing page performance, maximizing ROI.
8. What Do You Know About Conversion Optimization?
CRO involves analyzing user behavior, identifying barriers to conversion, and implementing changes to improve the likelihood of users completing specific goals. It combines data analysis, user experience (UX) design, and testing to optimize websites, landing pages, or apps. The conversion rate is calculated as:
Conversion Rate = (Number of Conversions / Total Visitors) × 100
For example, if a website gets 1,000 visitors and 50 complete a purchase, the conversion rate is 5%.
9. Explain The Difference Between Adwords & Adsense?
There are several points of differences between Adwords and Adsense that you mustang be well aware of. Some of the key differences of it are as follows:-
| Aspect | Adwords | Adsense |
|---|---|---|
| User | Advertisers (businesses, marketers). | Publishers (website owners, creators) |
| Purpose | Promote products/services, drive traffic | Monetize website/content with ads |
| Role | Create and manage ads | Display ads from Google’s network |
| Revenue | Spend money to advertise | Earn money from ad interactions |
| Control | High (ad creation, targeting, budget) | Limited (ad placement, format) |
| Goals | Traffic, leads, sales | Passive income from traffic |
| Requirements | Budget, account, landing page | Approved website/channel, traffic |
10. Explain The Importance Of Backlinks In SEO?
Backlinks, also known as inbound or incoming links, are hyperlinks from external websites pointing to your website. They are a critical component of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) because they signal a website’s authority, relevance, and trustworthiness to search engines like Google.
Why Backlinks Are Important in SEO
- Signal Authority and Trust:
- Backlinks act as “votes of confidence” from other websites, indicating that your content is valuable and credible.
- High-quality backlinks from authoritative sites (e.g., Forbes, industry leaders) boost your site’s Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-A-T), a key factor in Google’s ranking algorithm.
- Impact: Search engines rank pages with strong backlink profiles higher, as they are seen as trusted sources.
- Drive Organic Rankings:
- Backlinks are one of the top ranking factors in Google’s algorithm, alongside content and user experience.
- Pages with more high-quality backlinks typically rank higher for competitive keywords, as they demonstrate relevance and popularity.
- Impact: Improves visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs), increasing organic traffic.
- Increase Referral Traffic:
- Backlinks from relevant, high-traffic sites direct users to your website, providing an additional traffic source beyond search.
- Example: A backlink from a popular blog in your niche can drive targeted visitors to your site.
- Impact: Expands audience reach and supports digital marketing goals like lead generation.
- Enhance Domain Authority:
- Backlinks contribute to your website’s Domain Authority (DA) or Domain Rating (DR), metrics used by tools like Moz or Ahrefs to measure a site’s overall SEO strength.
- A strong backlink profile improves your ability to rank for a wide range of keywords.
- Impact: Higher DA makes it easier to compete in search results, even for new content.
- Facilitate Indexing:
- Backlinks help search engine crawlers discover your website and index its pages more efficiently.
- Impact: Speeds up the indexing process, ensuring new pages appear in search results faster.
11. What Do You Know About Automated Bidding Strategies?
Automated bidding strategies allow advertisers to delegate bid management to the advertising platform’s algorithms, which analyze data signals (e.g., user behavior, device, location, time) to set optimal bids for each ad auction.
Unlike manual bidding, where advertisers set specific bid amounts, automated bidding dynamically adjusts bids to achieve predefined objectives, such as increasing conversions or improving cost-efficiency.
Key Automated Bidding Strategies in Google Ads
Google Ads, the most widely used PPC platform, offers several automated bidding strategies, each tailored to specific campaign goals:
- Maximize Clicks:
- Goal: Drive as many clicks as possible within a budget.
- How It Works: Automatically sets bids to get the most clicks, prioritizing high-traffic opportunities.
- Use Case: Ideal for campaigns focused on increasing website traffic, such as brand awareness or content promotion.
- Maximize Conversions:
- Goal: Achieve the highest number of conversions within a budget.
- How It Works: Adjusts bids to prioritize ad placements likely to result in conversions (e.g., form submissions, purchases).
- Use Case: Suitable for lead generation or e-commerce campaigns with clear conversion goals.
- Maximize Conversion Value:
- Goal: Maximize the total value of conversions (e.g., revenue) within a budget.
- How It Works: Optimizes bids for higher-value conversions, focusing on users likely to generate more revenue.
- Use Case: Best for e-commerce businesses aiming to boost sales value.
- Target CPA (Cost Per Acquisition):
- Goal: Achieve conversions at a target cost per action.
- How It Works: Sets bids to meet a specified average CPA, balancing cost and conversion volume.
- Use Case: Effective for campaigns with specific cost-per-lead or cost-per-sale targets.
- Target ROAS (Return on Ad Spend):
- Goal: Achieve a target return on ad spend (e.g., $5 revenue for every $1 spent).
- How It Works: Adjusts bids to maximize conversion value while meeting the desired ROAS.
12. Differentiate Between Direct Marketing & Branding?
There are several points of differences between direct marketing and branding that you must be well aware of. So, let’s explore the key points in this regard.
| Aspect | Direct Marketing | Branding |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Immediate conversions (sales, leads) | Long-term awareness, loyalty, perception |
| Focus | Transactions, CTAs | Emotional connection, identity |
| Time Frame | Short-term results | Long-term impact |
| Channels | Email, PPC, SMS, direct mail | Social media, content, PR, sponsorships |
| Measurement | Conversion rate, CPA, CTR | Brand awareness, sentiment, loyalty |
| Audience | Specific, targeted segments | Broad, general audience |
| Content | Promotional, action-driven | Storytelling, value-driven |
| ROI | Immediate, measurable | Gradual, qualitative |
13. What Are The Disadvantages Of Digital Marketing?
There are some crucial limitations of digital marketing as well that you must be well aware off. Some of the core factors to consider it are as follows:-
Disadvantages of Digital Marketing
- High Competition and Saturation:
- Issue: The digital space is crowded, with countless businesses vying for attention on platforms like Google, social media, and email. Standing out requires significant effort and creativity.
- Impact: High competition can increase advertising costs (e.g., rising CPC in Google Ads) and make it harder to capture audience attention, especially for smaller businesses with limited budgets.
- Example: A new e-commerce store struggles to rank for competitive keywords like “online clothing” due to established brands dominating SERPs.
- Constant Algorithm Changes:
- Issue: Search engines (e.g., Google) and social media platforms frequently update their algorithms, affecting visibility and performance of campaigns.
- Impact: Strategies that work today (e.g., SEO tactics, ad placements) may become ineffective, requiring ongoing adaptation and learning.
- Example: A drop in organic reach on Instagram due to an algorithm prioritizing Reels over static posts.
- Time-Intensive and Resource-Heavy:
- Issue: Effective digital marketing demands time, expertise, and resources for content creation, campaign management, analytics, and optimization.
- Impact: Small businesses or teams with limited staff may struggle to keep up with the demands of multiple channels (SEO, PPC, social media).
- Example: A startup spends hours creating content but lacks the expertise to optimize it for SEO, delaying results.
- Dependence on Technology:
- Issue: Digital marketing relies heavily on platforms, tools, and internet connectivity, making it vulnerable to technical issues or outages.
- Impact: Downtime (e.g., website crashes, ad platform glitches) can disrupt campaigns and lead to lost opportunities or revenue.
- Example: A website outage during a PPC campaign results in wasted ad spend and missed conversions.
14. What Are The Advantages Of Digital Marketing?
There are several kinds of merits of digital marketing that most of us are not aware off. Some of the key advantages of digital marketing are as follows:-
- Cost-Effectiveness: Digital marketing is often more affordable than traditional channels like TV or print ads. Small businesses can reach large audiences with minimal budgets using tools like social media or email marketing.
- Targeted Reach: Platforms allow precise targeting based on demographics, interests, behaviors, or location, ensuring your message reaches the right audience.
- Measurable Results: Analytics tools provide real-time data on campaign performance, such as clicks, conversions, and engagement, enabling quick adjustments to optimize results.
- Global Reach: Digital marketing breaks geographical barriers, allowing businesses to connect with audiences worldwide through websites, social media, or search engines.
- Engagement and Interactivity: It enables two-way communication with customers via social media, comments, or live chats, fostering stronger relationships and brand loyalty.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Campaigns can be modified or scaled quickly based on performance or market changes, unlike rigid traditional media schedules.
- Higher ROI: With lower costs and precise targeting, digital marketing often delivers a higher return on investment compared to traditional methods.
- Personalization: Tailored content, such as personalized emails or ads, increases relevance and improves customer response rates.
- 24/7 Availability: Digital channels operate round-the-clock, allowing customers to engage with your brand anytime, increasing opportunities for sales and interaction.
- Brand Building: Consistent online presence through content marketing, SEO, and social media enhances brand visibility and authority over time.
15. What Are The Trends Of Digital Marketing This Year?
In 2025, digital marketing trends are driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer behaviors, and a focus on authenticity and efficiency. Below are the key trends shaping the digital marketing landscape this year, based on recent insights from industry sources:
- AI-Driven Personalization and Automation: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are central to digital marketing, powering hyper-personalized content and automating tasks like content creation, customer segmentation, and analytics.
- Rise of Zero-Click and AI-Enhanced Search: Search engines like Google and AI platforms like Perplexity and ChatGPT are transforming SEO with zero-click searches, where answers appear directly on search engine results pages (SERPs) via AI summaries or rich snippets.
- Short-Form Video Dominance: Short-form videos (under 90 seconds) on platforms like TikTok, Instagram Reels, and YouTube Shorts are the highest-ROI content type, with 2.5 times more engagement than long-form content. Brands are leveraging these for quick, authentic storytelling and interactive features like polls and live Q&As.coursera.orgsuperside.com
- Social Commerce and Influencer Marketing: Social media platforms are evolving into full ecosystems, integrating e-commerce and entertainment. Social commerce is projected to exceed $1 trillion by 2028, with platforms like Instagram (over 2 billion users) enabling direct purchases.
- Sustainability and Ethical Marketing: Consumers, with 85% affected by climate change, demand transparency and sustainability. Brands are prioritizing ethical practices, with EU regulations mandating clear sustainability reporting. Campaigns reflecting genuine environmental and social responsibility resonate strongly.
Few related topics for your knowledge
- 50 Important Interview Questions & Answers On Google Ads
- 30 Important SEO Glossary Terms For Interview Preparation
- How Countries Are Integrating AI Into School Curriculums — Is India Falling Behind?
- Digital Marketing Executive Job Description
- 25 Effective Bid Strategies In Google Ads To Maximize ROI
16. What Are The Popular Digital Marketing Tools?
In 2025, digital marketing tools are essential for streamlining campaigns, analyzing data, and enhancing customer engagement. It is one of Below is a list of popular digital marketing tools across various functions, based on current industry insights:
- Google Analytics 4 (GA4):
- Function: Web and app analytics
- Why Popular: Tracks user behavior, conversions, and website performance with advanced AI-driven insights. It’s free for basic use, widely adopted, and integrates with other Google tools like Google Ads.
- Use Case: Measuring website traffic, user journeys, and campaign ROI.
- HubSpot:
- Function: CRM, marketing automation, and content management
- Why Popular: Offers an all-in-one platform for email marketing, lead nurturing, and analytics with robust free and paid plans. Used by over 200,000 businesses for its scalability.
- Use Case: Managing customer relationships and automating email workflows.
- Semrush:
- Function: SEO, content marketing, and competitor analysis
- Why Popular: Provides keyword research, site audits, and backlink analysis, with over 10 million users globally. Its AI tools help optimize for zero-click searches and voice queries.
- Use Case: Improving search engine rankings and content strategy.
- Ahrefs:
- Function: SEO and backlink analysis
- Why Popular: Known for its comprehensive backlink database and site explorer, used by 1.5 million marketers. It excels in competitor research and keyword tracking.
- Use Case: Identifying link-building opportunities and tracking SEO performance.
- Hootsuite:
- Function: Social media management
- Why Popular: Schedules posts across multiple platforms, monitors engagement, and provides analytics. Supports over 35 social networks, ideal for teams managing social commerce.
- Use Case: Streamlining social media campaigns and tracking brand mentions.
17. How To Categorize Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing can be categorized based on its strategies, channels, or objectives, providing a structured approach to planning and execution. Below are the primary ways to categorize digital marketing, focusing on the most common frameworks used in 2025:
1. By Strategy Or Approach
This categorization focuses on the overarching methods used to achieve marketing goals:
- Inbound Marketing: Attracts customers through valuable content and organic engagement. Interview questions for digital marketing can help you to meet your needs with ease.
- Examples: Content marketing, SEO, social media engagement.
- Goal: Build trust and long-term relationships by providing useful information.
- Outbound Marketing: Actively reaches out to audiences through paid or direct methods.
- Examples: PPC ads, email blasts, display advertising.
- Goal: Generate immediate leads or sales through direct promotion.
- Performance Marketing: Focuses on measurable results and ROI-driven campaigns.
- Examples: Affiliate marketing, paid search, social media ads.
- Goal: Optimize campaigns based on data and conversions.
- Brand Marketing: Emphasizes building brand awareness and loyalty.
- Examples: Storytelling, influencer partnerships, video campaigns.
- Goal: Strengthen brand identity and emotional connection.
2. By Channel Or Platform
This categorizes digital marketing based on the mediums used to reach audiences:
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM):
- Includes SEO (organic search optimization) and PPC (paid search ads like Google Ads).
- Focus: Increase visibility on search engines.
- Social Media Marketing:
- Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, LinkedIn, and Threads (2 billion+ users on Instagram alone).
- Focus: Engagement, social commerce, and influencer collaborations.
- Email Marketing:
- Personalized campaigns, newsletters, and drip sequences (e.g., via Mailchimp).
- Focus: Direct communication and customer retention.
- Content Marketing:
- Blogs, videos, infographics, and podcasts (short-form video drives 2.5x more engagement).
- Focus: Educate and attract audiences with valuable content.
- Affiliate Marketing:
- Partnerships with influencers or websites to promote products for commissions.
- Focus: Expand reach through third-party endorsements.
- Mobile Marketing:
- SMS, push notifications, and in-app ads (over 6 billion smartphone users globally).
- Focus: Target users on mobile devices. It is one of the crucial interview questions for digital marketing to meet your goals with ease.
- Display Advertising:
- Banner ads, retargeting, and native ads (e.g., via retail media networks).
- Focus: Visual promotion across websites and apps.
- Connected TV (CTV) and Video Marketing:
- Ads on streaming platforms and short-form videos on YouTube Shorts or TikTok.
- Focus: Engage audiences through immersive video content.
3. By Objective Or Goal
This categorizes digital marketing based on the intended outcome:
- Lead Generation: Attract potential customers through forms, landing pages, or gated content.
- Examples: Email sign-ups, webinars, free trials.
- Brand Awareness: Increase visibility and recognition among target audiences.
- Examples: Social media campaigns, viral videos, PR stunts.
- Customer Acquisition: Convert leads into paying customers.
- Examples: PPC campaigns, e-commerce promotions, retargeting ads.
- Customer Retention and Loyalty: Engage existing customers to encourage repeat business.
- Examples: Email nurturing, loyalty programs, personalized offers.
- Engagement and Community Building: Foster interaction and build communities around the brand.
- Examples: Social media challenges, user-generated content, forums.
4. By Audience Targeting Method
This focuses on how audiences are segmented and reached:
- Demographic Targeting: Based on age, gender, income, etc.
- Example: Ads tailored for Gen Z on TikTok.
- Behavioral Targeting: Based on user actions, like browsing or purchase history.
- Example: Retargeting ads for abandoned carts.
- Geographic Targeting: Based on location (local, regional, or global).
- Example: Local SEO for small businesses.
- Psychographic Targeting: Based on interests, values, or lifestyles.
- Example: Sustainability-focused campaigns for eco-conscious consumers.
5. By Technology Or Innovation
Reflecting 2025 trends, this categorizes based on emerging tools and technologies:
- AI-Driven Marketing: Uses AI for personalization, automation, and analytics.
- Examples: AI-generated content, predictive analytics (used by 70%+ of marketers).
- Immersive Marketing: Leverages AR/VR for interactive experiences.
- Examples: Virtual product try-ons, VR showrooms (VR market projected at $435B by 2030).
- Voice Search Marketing: Optimizes for voice queries (1 billion+ monthly voice searches).
- Examples: Conversational keywords, FAQ schema.
- Zero-Click Search Optimization: Focuses on featured snippets and AI-driven SERPs.
- Examples: Structured data, answer-box content.
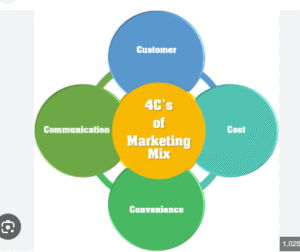
18. What Are The 4 C’s Of Digital Marketing?
The 4 C’s of marketing is a customer-centric framework that shifts the focus from the traditional 4 P’s (Product, Price, Place, Promotion) to better align with modern consumer behavior and digital marketing trends. The 4 C’s are:
- Customer (or Consumer Value):
- Definition: Focuses on understanding the customer’s needs, wants, and preferences to deliver value through products or services.
- Example: A brand uses AI-driven insights to recommend products based on browsing history, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Cost (to the Customer):
- Definition: Considers the total cost to the customer, including price, time, effort, and opportunity cost, rather than just the monetary price.
- Example: Offering free shipping or a one-click checkout reduces the perceived cost of buying online.
- Convenience:
- Definition: Emphasizes making the purchase process easy and accessible across channels, aligning with the customer’s preferred platforms and devices.
- Example: A retailer integrates “Buy Now” buttons on Instagram Reels. Thus, it allows instant purchases from short-form videos.
- Communication:
- Definition: Replaces traditional promotion with two-way, authentic engagement through storytelling, social media, and personalized content.
- Example: A brand runs a TikTok campaign with user-generated content, fostering dialogue and building community.
19. Differentiate Between Do Follow And No Follow Links?
There are several points of differences between Do Follow and No Follow Links. Some of the key points to follow in this case are as follows:-
| Aspects | Do Follow Links | No Follow Links |
|---|---|---|
| Crawlability | It permits all the search engine indexing and crawling | This instructs search engines not to follow any link that limits the indexing process. |
| Link Juice Transfer | To the destination page it passes the link juice. | It prevents the transfer of authority which signals the linked content must not impact the rankings. |
| Search Engine Rejection | It implies all the linked content to the source. | It does not reject all the linked content thus signalling potential rejection and its lack. |
| Use Cases | Editorial content, guest posts, trusted external links endorsing content. | Untrusted content, sponsored links, affiliate links, user-generated content (e.g., comments). |
| Impact On SEO | Boosts linked site’s search engine ranking by transferring authority. | Does not influence SEO ranking, as search engines ignore for ranking purposes. |
| Traffic Impact | Drives traffic and improves search visibility due to SEO benefits. | Drives traffic only through user clicks, no SEO benefit. |
| Examples | Links in high-quality blog posts or articles citing authoritative sources. | Links in social media posts, forum comments, or sponsored content. |
Source( Mangools.com)

Source( Mangools.com)
20. What Is A 301 Redirect?
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect that automatically sends users and search engine crawlers from one URL to another. It indicates that a webpage has been permanently moved to a new location, passing most of the original page’s link equity (SEO value) to the new URL.
Key Points:
- Status Code: HTTP 301 (Moved Permanently).
- Purpose: Used when a webpage is relocated permanently, such as when updating a website’s structure, changing domains, or consolidating pages.
- SEO Impact: Transfers 90-99% of the original page’s link authority to the new URL, preserving search engine rankings.
- Use Cases:
- Redirecting old URLs after a site redesign.
- Moving a site to a new domain.
- Handling duplicate content by redirecting to a preferred URL.
- Migrating from HTTP to HTTPS.
- Implementation: Can be set up via server-side configuration (e.g., .htaccess for Apache, nginx.conf for Nginx) or through CMS plugins (e.g., WordPress plugins like Yoast SEO).
- Example:
- Old URL: http://example.com/old-page
- Redirects to: http://example.com/new-page
- Code in .htaccess: Redirect 301 /old-page /new-page
21. What Are The Best Practices To Rank YouTube Channels?
To rank a YouTube channel effectively, you need to optimize both your videos and channel for YouTube’s search algorithm, enhance user engagement, and promote content strategically.
1. Conduct Thorough Keyword Research
- Why: Keywords help YouTube understand your video content and match it to user search queries, improving discoverability.
- How:
- Use YouTube’s Search Suggest feature to identify popular search terms by typing a word or phrase into the YouTube search bar.backlinko.com
- Leverage tools like TubeBuddy, VidIQ, or Keyword.io to find high-volume, low-competition keywords. For example, target long-tail keywords (e.g., “how to train a dog to walk on a leash” vs. “dog training”).
2. Optimize Video Titles
- Why: Titles are a primary ranking factor, influencing click-through rates (CTR) and relevance.
- How:
- Include your target keyword early in the title (within the first 1-2 words).lseo.comrankmath.com
- Keep titles concise (6-10 words) and descriptive to align with search intent.
3. Write Detailed Video Descriptions
- Why: Descriptions provide context to YouTube’s algorithm and can help rank for related search terms.
- How:
- Write long descriptions (250+ words, ideally 1-2 paragraphs) with your target keyword in the first 25 words and repeated naturally 3-4 times.backlinko.comwebfriendly.com
- Include a video synopsis, a call-to-action (CTA) to subscribe or visit your website, and links to relevant resources.
4. Use Relevant Tags
- Why: Tags help YouTube categorize your video and increase chances of appearing in search and suggested video sections.
- How:
- Use 2-3 tags with your target keyword and close variations, 2 tags describing the video’s topic, and 1-2 tags for your industry/vertical.backlinko.com
- Copy competitor tags for similar content to appear in related video sidebars.
22. What Is Mobile First Indexing?
Mobile-First Indexing is a Google search engine practice where the mobile version of a website is prioritized for indexing and ranking in search results. Instead of primarily using the desktop version of a site to determine its relevance, Google’s crawlers use the mobile version as the primary source for indexing content and evaluating user experience.
- Definition: Google indexes and ranks a website based on its mobile version’s content, structure, and performance, even for desktop searches.
- Why It Matters: With most internet users accessing websites via mobile devices (over 60% of searches are mobile), Google aims to deliver a consistent and optimized experience for mobile users.
- Implementation: Introduced in 2016 and fully rolled out by 2021, mobile-first indexing is now the default for all websites.
- Impact on SEO:
- Websites with poor mobile versions (e.g., slow loading, non-responsive design, or missing content) may rank lower.
- Mobile-friendly sites with responsive design, fast load times, and identical content across devices perform better.
23. List The Most Popular Local SEO Ranking Factors?
Local SEO ranking factors determine how well a business ranks in local search results, such as Google’s Local Pack, Maps, or organic listings.
1.Google Business Profile (GBP) Optimization
- Why: A fully optimized GBP is critical for appearing in the Local Pack and Google Maps.
- Key Actions:
- Claim and verify your GBP listing.
- Complete all fields: business name, address, phone number (NAP), categories, hours, and description.
- Use primary and secondary categories that align with your services (e.g., “Dentist” as primary, “Cosmetic Dentist” as secondary).
- Add high-quality photos (e.g., storefront, interior, products) and update regularly.
- Impact: A complete and accurate GBP signals relevance and trustworthiness to Google.
2. NAP Consistency (Name, Address, Phone Number)
- Why: Consistent NAP across all online platforms builds trust and helps Google verify your business’s legitimacy.
- Key Actions:
- Ensure NAP is identical on GBP, website, social media, and directories (e.g., Yelp, Yellow Pages).
- Use tools like Moz Local or BrightLocal to audit and fix inconsistencies.
- Impact: Inconsistent NAP can confuse Google, lowering rankings or causing listing errors.
3. Proximity to the Searcher
- Why: Google prioritizes businesses closer to the user’s location for local queries (e.g., “coffee shop near me”).
- Key Actions:
- Optimize for hyper-local keywords (e.g., “coffee shop in [neighborhood]”).
- Ensure your GBP address is accurate and pinned correctly on Google Maps.
- Impact: Proximity is a strong ranking factor for “near me” searches, though it’s less controllable.
4. Reviews and Ratings
- Why: Positive reviews and high ratings signal credibility and user satisfaction, influencing both rankings and user trust.
- Key Actions:
- Encourage customers to leave reviews on GBP, Yelp, and other platforms (e.g., via email follow-ups or QR codes).
- Respond to all reviews (positive and negative) professionally to show engagement.
- Impact: Review quantity, quality, and recency directly boost Local Pack rankings.
24. How To Avoid Content Penalty For Duplicates?
There are some steps you need to take for avoiding the content penalty for duplicates. Some of the key steps that you must adopt are as follows:-
| Practice | Actionable Steps | Tools |
|---|---|---|
| 301 redirects | Redirect duplicate URLs to a single version via .htaccess, Nginx, or CMS plugins. | Screaming Frog, Yoast SEO |
| Canonical Tags | Add rel=”canonical” to preferred URLs for similar pages. | Yoast SEO, Rank Math |
| Robot.txt/ No index | Block non-essential pages from indexing. | Google Search Console |
| Mobile Content Parity | Ensure identical content on mobile/desktop for mobile-first indexing. | Mobile-Friendly Test |
| Unique Content | Write unique titles, descriptions, and content for similar pages. | Semrush, Ahrefs |
| Syndicated Content | Rewrite content, use canonicals, or request no follow links. | Copyscape |
| URL Parameters | Ignore irrelevant parameters in Search Console, use canonicals. | Google Search Console |
| Regular Audit | Crawl site for duplicates, monitor Search Console for errors. | Screaming Frog, Semrush, Ahrefs |
| Structured Data | Add schema to clarify page intent. | Rich Results Test |
25. What Are The Ways You Can Increase Web Page Speed?
Increasing web page speed is critical for improving user experience, boosting SEO rankings (especially with mobile-first indexing), and reducing bounce rates. Faster pages align with Google’s Core Web Vitals (e.g., Largest Contentful Paint, Interaction to Next Paint, Cumulative Layout Shift), which are key ranking factors in 2025.
1. Optimize Images
- Why: Large, unoptimized images are a primary cause of slow page load times, especially on mobile devices. It is one of the crucial interview questions for digital marketing candidates during the interview process.
2. Minimize and Optimize Code
- Why: Bloated HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files slow down rendering and execution.
3. Leverage Browser Caching
- Why: Caching stores static files locally, reducing server requests for returning visitors.
4. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Why: CDNs distribute content across global servers, reducing latency by serving files from the nearest location.
5. Optimize Server Response Time
- Why: Slow server response times increase TTFB, delaying page rendering.
6. Enable Lazy Loading for Non-Critical Resources
- Why: Lazy loading defers loading of offscreen images, videos, or iframes until needed, reducing initial load time. It is a crucial interview questions for digital marketing
26. When Should Short Tail And Long Tail Keywords Be Targeted?
There are some techniques that you need to follow for targeting the short tail and long tail keywords. Now, when to target short tail keywords and when to target long tail keywords there are some way out that you must follow:-
When To Target Short Tail Vs Long Tail Keywords
| Aspects | Short Tail Keywords | Long Tail Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | 1-2 words, broad (e.g., “pizza delivery”) | 3+ words, specific (e.g., “vegan pizza delivery Chicago”) |
| Search Volume | High (thousands-millions) | Low (hundreds or fewer) |
| Competition | High, dominated by authoritative sites | Low, easier to rank for new sites |
| Conversion Rate | Lower, vague intent | Higher, specific intent |
| When to target | Established sites, brand awareness, broad local queries | New sites, niche audiences, conversions, hyper-local |
| Best Use Case | Homepage, category pages, pillar content, YouTube playlists | Blog posts, product/service pages, location pages, YouTube tutorials |
| SEO Effort | High (needs backlinks, authority) | Lower (quick wins, less competition) |
| Tools | Google Keyword Planner, Semrush, Ahrefs | TubeBuddy, AnswerThePublic, Google Search Suggest |
27. What Are The Most Effective Ways To Increase Traffic On Your Website?
Increasing website traffic is a multifaceted process that leverages SEO, content marketing, social media, and other strategies to attract and retain visitors.
- Optimize for Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- Create High-Quality, Engaging Content
- Leverage YouTube and Video Content
- Utilize Social Media Marketing
- Build High-Quality Backlinks
- Improve Website Speed and User Experience
- Run Paid Advertising Campaigns
- Leverage Email Marketing
It is one of the crucial interview questions for digital marketing. This can boost the scope of your brand value in the long run.
28. What Are The On-Page & Off-Page Optimization?
There are several points of differences between On Page & Off Page optimization. Let’s get through the details to have a better idea of it. So, let’s explore the essential differences between the two:-
| Aspects | On Page Optimization | Off- Page Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Techniques applied directly on the website to improve its search engine ranking and user experience. | Activities performed outside the website to boost its authority, reputation, and visibility. |
| Focus | Content, technical structure, and user experience within the site. | Building external signals like backlinks, social mentions, and brand reputation. |
| Control | Full control, as it involves changes to your own website. | Partial control, as it relies on external entities (e.g., other websites, users). |
| Key Components | – Content optimization (keywords, quality)
– Meta tags (title, description) – URL structure – Internal linking – Site speed – Mobile-friendliness – Schema markup |
– Backlinks (do follow/no follow, as discussed)
– Social media engagement – Local citations (for Local SEO) – Guest posting – Brand mentions – Reviews/ratings |
| Examples | – Optimizing title tags with short-tail/long-tail keywords (e.g., “Best Dentist in [City]”).
– Adding schema markup to clarify content (as in duplicate content). – Improving web page speed (e.g., image compression, lazy loading). – Using 301 redirects to fix broken URLs. – Ensuring mobile-first indexing compliance. |
Earning do follow backlinks from local news sites (as in Local SEO).
– Sharing YouTube videos on social media for YouTube SEO. – Building citations on Yelp for Local SEO. – Encouraging GBP reviews. – Guest blogging on industry sites with do follow links. |
29. What Is AMP?
- Definition: AMP is a framework that enables the creation of lightweight web pages designed to load almost instantly on mobile devices, improving user experience and aligning with mobile-first indexing.
- Purpose: To enhance mobile web performance, reduce bounce rates, and improve SEO by meeting Core Web Vitals (e.g., Largest Contentful Paint, Cumulative Layout Shift).
- How It Works:
- Uses AMP HTML, a simplified version of HTML with custom tags (e.g., <amp-img> instead of <img>).
- Limits JavaScript to AMP’s optimized library, reducing render-blocking scripts.
- Leverages AMP Cache (e.g., Google AMP Cache) to pre-render and serve pages from a CDN, boosting speed.
- Prioritizes above-the-fold content for instant loading.
30. What Is The Use Of Anchor Tags In SEO?
Anchor tags () in SEO are HTML elements used to create hyperlinks that connect one page to another, either within the same website (internal links) or to external websites. They play a significant role in search engine optimization by influencing site structure, user navigation, link equity distribution, and search engine crawling.
- Facilitate Search Engine Crawling and Indexing
- Distribute Link Equity (PageRank)
- Improve Site Structure and Navigation
- Enhance Keyword Relevance with Anchor Text
- Drive Traffic and Engagement
- Support Local SEO and External Linking
- Avoid Duplicate Content Issue
31. Explain The Significance Of CTR?
Click-Through Rate (CTR) is a key metric in digital marketing and SEO, representing the percentage of users who click on a link, ad, or search result after seeing it. It’s calculated as:
CTR = (Number of Clicks ÷ Number of Impressions) × 100
- Indicator of Relevance and Appeal
- Why: A high CTR signals that your title, meta description, or ad copy aligns with user search intent, making it relevant and enticing.
- Context:
-
- In Local SEO, a high CTR on Google Business Profile (GBP) listings (e.g., “Call Now” or “Directions”) indicates strong local relevance (e.g., for “dentist in [city]”).
- In YouTube SEO, compelling video titles and thumbnails (optimized with short-tail/long-tail keywords) drive higher CTR, boosting video rankings.
- Drives Organic and Paid Traffic
- Why: Higher CTR directly increases clicks, leading to more website or video views, a key goal in increasing traffic.
- Context:
- Optimized meta titles/descriptions with short-tail/long-tail keywords (e.g., “emergency plumber [city]”) improve organic CTR in search results.
- Fast-loading pages (as discussed in web page speed and AMP) and mobile-first indexing compliance ensure users click and stay, reducing bounce rates.
- Influences Search Engine Rankings
- Why: Google uses CTR as a behavioral signal to assess content quality. Pages with above-average CTR for their position tend to rank higher.
- Context:
- On-page optimization: Keyword-rich titles, meta descriptions, and schema markup (e.g., star ratings in search results) boost CTR.
- YouTube SEO: High CTR on video thumbnails/titles signals engagement, improving video rankings in search and suggested videos.
- Improves User Engagement Metrics
- Why: High CTR correlates with better engagement (e.g., dwell time, page views), as users are more likely to interact with relevant content.
- Context:
- Internal anchor tags (as discussed) guide users to high-value pages, increasing engagement and supporting on-page optimization.
32. What Can You Do To Improve The Conversion Rate?
Improving the Conversion Rate (CR)—the percentage of visitors who complete a desired action (e.g., purchase, form submission, sign-up)—is critical for maximizing the effectiveness of your website traffic. A higher CR means more users turn into customers or leads, directly impacting revenue and ROI.
Strategies to Improve Conversion Rate
- Optimize for User Experience (UX)
- Enhance Page Load Speed
- Target High-Intent Keywords
- Improve Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Create Targeted Landing Pages
- Leverage Trust Signals
- Optimize for Local SEO
33. Explain What Google Adwords Is?
Google AdWords, now known as Google Ads, is Google’s online advertising platform that allows businesses, marketers, and individuals to create and display ads across Google’s ecosystem, including search results, websites, mobile apps, and videos (e.g., YouTube). It operates on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, where advertisers bid on keywords to show their ads to targeted audiences.
How It Works:
- Advertisers bid on short-tail/long-tail keywords (as discussed) to display ads when users search for those terms.
- Ads are shown based on relevance, bid amount, and Quality Score (a metric based on ad relevance, CTR, and landing page quality).
- Payment is typically per click (PPC), though other models like cost-per-impression (CPM) or cost-per-action (CPA) are available.
34. Can You Tell Us About Few Google Adwords And Few Google Ad Extensions Name?
Google AdWords, now called Google Ads, is Google’s advertising platform that enables businesses to create targeted ads across Google Search, YouTube, Google Display Network (GDN), and other platforms, primarily using a pay-per-click (PPC) model. Google Ads extensions, now referred to as assets, are additional pieces of information added to ads to enhance visibility, engagement, and click-through rate (CTR), providing more context about your business.
- Sitelink Extensions
- Call Extensions
- Location Extensions
- Structured Snippet Extensions
- Call Out Extensions
35. How Google Ad Ranks?
Google Ads ranking determines the position and visibility of your ads on Google Search, Display Network, YouTube, and other platforms within Google’s ecosystem. The ranking is primarily based on a combination of your bid, Quality Score, and the expected impact of ad extensions (assets).
Key Factors Affecting Ad Rank
- Bid Amount.
- Quality Score.
- Expected Impact On Ad Extensions.
- Context Of the User Reach.
- Competition in auction.
36. What Is Ad Scheduling?
Ad scheduling, also known as dayparting in Google Ads, is a feature that allows advertisers to control when their ads are displayed based on specific days of the week or times of day. This helps optimize ad performance by targeting audiences when they are most likely to engage or convert, improving click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, and cost efficiency.
- Purpose: To maximize ROI by focusing ad spend on high-performing time slots, reducing wasted impressions, and aligning with user behavior.
- How Does It Work?
- Advertisers set schedules in the Google Ads platform at the campaign or ad group level.
- Ads can be shown or paused based on time zones, days (e.g., Monday-Sunday), or hours (e.g., 9 AM-5 PM).
- Bid adjustments can be applied to increase or decrease bids during specific time slots to prioritize high-conversion periods.
37. What Are The Different Ad Formats Available On Google Ads?
Google Ads offers a variety of ad formats to help businesses reach their target audience across Google’s ecosystem, including Search, Display Network, YouTube, and partner platforms.
Each format serves specific goals, such as driving click-through rate (CTR), conversions, traffic, or brand awareness, and aligns with strategies like Local SEO, YouTube SEO, mobile-first indexing, web page speed, short-tail/long-tail keywords, on-page/off-page optimization, AMP, anchor tags, conversion rate, ad extensions, Google Ads rank, CTR calculation, and ad scheduling, as discussed in your previous questions
Different Types Of Google Ad Formats Are as Follows:-
- Search ads
- Display ads
- Video Ads
- Shopping Ads
- Local Service Ads
- App Promotion ads
38. What Is RSLA And How It Works?
RSLA, or Responsive Search Ads Location Extensions, is not a standard term in Google Ads or SEO as of 2025. However, based on your previous questions (e.g., Local SEO, Google AdWords, ad extensions, CTR, Google Ads rank, ad scheduling, conversion rate, etc.) and the context of Google Ads.
Working Mechanism Of RSLA
- RSA Setup: Advertisers create an RSA in Google Ads by entering multiple headlines (3-15, up to 30 characters) and descriptions (2-4, up to 90 characters). These “assets” are mixed and matched by Google’s AI to form ad combinations that best match user queries.support.google.com
- Example: For a plumber, headlines might include “24/7 Plumber in {City},” “Emergency Plumbing [City],” “Top-Rated Local Plumber,” and descriptions like “Fast Service, Call Now!” or “Serving [City] Area.”
- Location Insertion: Within RSA headlines or descriptions, advertisers insert a code like {LOCATION(City)} to dynamically display the user’s city, state, or country based on their location or search intent (e.g., “Plumber in Seattle” for a Seattle user). Default text (e.g., “Your City”) is set for cases where location data is unavailable or exceeds character limits (30 for headlines, 90 for descriptions).
- Google’s AI Matching: When a user searches (e.g., “emergency plumber near me”), Google’s AI evaluates the RSA’s headlines, descriptions, and keywords (including short-tail/long-tail keywords, as discussed). It selects the combination predicted to maximize CTR and relevance, factoring in:
- User’s search query (e.g., “plumber Seattle”).
- Location data (physical location or interest, e.g., Seattle).
- Device type (aligned with mobile-first indexing).
- Time of day (aligned with ad scheduling).
- Google’s Learning: Over time, Google’s AI analyzes performance data (clicks, impressions, conversions) to favor high-performing headline/description combinations, improving CTR and Google Ads rank.
39. What Types Of Audiences Can Be Used In GDN?
The GDN allows advertisers to target audiences based on their interests, behaviors, demographics, and interactions with your business. Here are the primary audience types, as outlined in sources like Google Ads Help and industry guides:
- Affinity audiences.
- In Market audiences.
- Custom audiences.
- Remarketing audiences
- Similar audience
- Demographic targeting
- Life events
40. What Are The Types Of Keywords Matching Available In Google Ads?
Interviewers often ask these interview questions for digital marketing regarding the types of keywords. Some of the common form of keywords that you must be well aware off are as follows:-
- Broad match
- Exact match
- Phrase Match
- Negative Keywords
41. What Are Some Reasons As To Why Ads Could Be Rejected?
Ads can be rejected for various reasons, depending on the platform’s policies. Here are common reasons based on general advertising guidelines, including insights from platforms like X:
- Violation of Content Policies: Ads containing prohibited content such as hate speech, violence, adult content, or discriminatory material are often rejected. For example, X’s ads policy prohibits content promoting illegal activities or graphic violence.
- Misleading or False Information: Ads with deceptive claims, exaggerated benefits, or misinformation (e.g., fake health cures or scams) are typically disallowed to protect users.
- Inappropriate Visuals or Language: Ads with explicit imagery, offensive language, or culturally insensitive content may be rejected for failing to meet community standards.
- Technical Issues: Ads not meeting technical requirements, such as incorrect image sizes, unsupported file formats, or broken links, can be rejected. For instance, X requires specific image dimensions and file types for ads.
- Targeting Restrictions: Ads targeting sensitive demographics (e.g., based on race, religion, or health conditions) or violating privacy rules may be disallowed.
- Prohibited Products or Services: Ads promoting restricted items like drugs, weapons, or counterfeit goods are commonly rejected. X, for example, bans ads for certain regulated products like alcohol in specific regions.
- Poor Quality or Relevance: Low-quality ads (e.g., blurry images, grammatical errors) or those irrelevant to the audience may be rejected to maintain user experience.
42. What Are The Different Kinds Of Bidding Available?
The types of bidding available for advertising depend on the platform, but based on common digital advertising practices and insights from platforms like X, here are the primary bidding strategies typically offered:
- Cost Per Click (CPC): You pay only when someone clicks on your ad. Ideal for driving traffic to a website or landing page. For example, X offers CPC bidding for campaigns focused on link clicks.
- Cost Per Mille (CPM): You pay for every 1,000 impressions (views) of your ad, regardless of clicks. This is suited for increasing brand visibility. X uses CPM for campaigns aiming to maximize reach.
- Cost Per Action (CPA): You pay when a specific action is completed, such as a purchase, sign-up, or form submission. This is common in performance-driven campaigns but may not be available on all platforms.
- Cost Per View (CPV): You pay for each view of a video ad, often used in video advertising platforms. X may apply this for promoted video content to boost engagement.
- Automated Bidding: Platforms like X offer automated bidding, where the system optimizes bids to achieve goals (e.g., maximum clicks or impressions) within your budget. This is often called “Optimized CPM” or “Auto-bid” and adjusts dynamically based on performance.
- Manual Bidding: You set a specific bid amount for clicks or impressions, giving you more control. X allows manual CPC or CPM bids for advertisers wanting precise budget management.
43. What Are Some Automatic Bidding Strategies?
Automatic bidding strategies are methods where advertising platforms optimize bids to achieve specific campaign goals within a set budget, minimizing manual adjustments. Based on common digital advertising practices and insights from platforms like X, here are some prevalent automatic bidding strategies:
- Maximize Clicks: The platform automatically adjusts bids to get the most clicks possible within your budget. Ideal for driving traffic to a website or landing page. For example, X’s automated bidding may prioritize clicks for campaigns focused on link engagement.
- Maximize Impressions (Reach): The system optimizes bids to show your ad to as many people as possible, often using a Cost Per Mille (CPM) model. This is suited for brand awareness campaigns, and X commonly uses this for reach-focused objectives.
- Target Cost Per Action (tCPA): The platform sets bids to achieve a target cost for specific actions, like conversions (e.g., sign-ups or purchases). It balances cost efficiency with goal achievement, though not all platforms, including X, always offer tCPA explicitly.
- Maximize Conversions: The system adjusts bids to drive the highest number of conversions within your budget, prioritizing users likely to complete actions like form submissions or purchases. X may use this for campaigns with conversion tracking enabled.
- Enhanced Cost Per Click (eCPC): The platform automatically adjusts your manual CPC bids to target users more likely to convert, balancing cost and performance. This is common in platforms like Google Ads and may be supported in X’s optimization tools.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): The system optimizes bids to maximize revenue or value from conversions relative to your ad spend. This is more advanced and typically requires conversion value tracking, which may be available in X’s premium ad tools.
44. What Is The Quality Score In Google Ads?
The Quality Score in Google Ads is a metric used to evaluate the quality and relevance of your ads, keywords, and landing pages. It’s reported on a scale of 1 to 10 (1 being the lowest, 10 the highest) and is calculated based on three main factors:
- Expected Click-Through Rate (CTR): How likely your ad is to be clicked based on historical performance and relevance to the search query.
- Ad Relevance: How closely your ad matches the intent of the user’s search query.
- Landing Page Experience: How relevant, user-friendly, and well-optimized your landing page is (e.g., fast loading, mobile-friendly, clear content).
45. What Are The Hallmarks Of A Good PPC Landing Page?
A good PPC (Pay-Per-Click) landing page is designed to maximize conversions by being relevant, user-friendly, and aligned with the ad’s intent. Based on best practices in digital advertising, here are the key hallmarks of an effective PPC landing page:
- Relevance to the Ad: The landing page content should match the ad’s message, keywords, and user intent. For example, if the ad promotes a specific product, the landing page should focus on that product, not a generic homepage.
- Clear and Compelling Headline: A concise, benefit-driven headline grabs attention and reinforces the ad’s promise (e.g., “Save 50% on Your Subscription Today!”).
- Strong Call-to-Action (CTA): A prominent, action-oriented CTA (e.g., “Buy Now,” “Sign Up Free”) guides users toward conversion. It should be visually distinct and repeated if necessary.
- Fast Loading Speed: Pages should load quickly (ideally under 3 seconds) to reduce bounce rates. Google’s PageSpeed Insights can help optimize performance.
- Mobile Optimization: The page must be responsive, ensuring seamless functionality and readability on mobile devices, as many PPC clicks come from mobile users.
- Minimalist Design: Clean, uncluttered layouts with focused visuals and minimal distractions (e.g., no excessive navigation links) keep users focused on the conversion goal.
- Trust Signals: Elements like customer testimonials, reviews, trust badges (e.g., SSL certificates), or guarantees (e.g., “30-Day Money-Back”) build credibility.
- Relevant and Engaging Content: Concise copy that highlights benefits, addresses pain points, and aligns with the user’s search intent. Avoid lengthy text or irrelevant details.
- Optimized Forms: If collecting user information, forms should be short, asking only for essential details (e.g., name and email) to reduce friction.
46. What Is The Difference Between Hard And Soft Bounce Emails?
There are some core points of differences between soft and hard bounce emails. Some of the key points of differences of it are as follows:-
| Aspect | Hard Bounce Emails | Soft Bounce Emails |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permanent delivery failure; email cannot be delivered to the recipient. | Temporary delivery failure; email cannot be delivered at the moment. |
| Cause | Invalid, non-existent, or deactivated email address; invalid domain. | Temporary issues like full inbox, server downtime, or message size limits. |
| Examples | Email address doesn’t exist – Domain doesn’t exist – Account closed |
Recipient’s inbox full – Server temporarily unavailable – Email too large |
| Delivery Impact | Email is undeliverable; no further delivery attempts are made. | Email may be deliverable later; retries often attempted. |
| Action Needed | Remove the email address from the mailing list to prevent future bounces. | Monitor; retries may resolve the issue, or check for recurring problems. |
| Sender Reputation impact | Repeated hard bounces can damage sender reputation and deliverability. | Minimal impact unless soft bounces persist frequently. |
| Frequency | Permanent issue; indicates a fundamental problem with the email address. | Temporary issue; may resolve without intervention. |
| Handling By USPS | Email platforms (e.g., Mailchimp, SendGrid) typically suppress hard bounces. | Platforms may retry delivery for a set period before marking as failed. |
47. How Do You Improve The Click Through Rate Of Your Email?
Improving the Click-Through Rate (CTR) of your email campaigns involves optimizing various elements to make your emails more engaging and relevant to your audience. Based on email marketing best practices, here are actionable strategies to boost CTR:
- Craft Compelling Subject Lines:
- Keep subject lines concise (under 60 characters) and compelling to grab attention.
- Use personalization (e.g., including the recipient’s name) or urgency (e.g., “Last Chance: 50% Off Ends Tonight!”).
- Avoid spammy words like “free” or excessive punctuation to prevent landing in spam folders.
- Personalize Email Content:
- Tailor emails based on user data (e.g., past purchases, location, or behavior) to increase relevance.
- Use dynamic content to show different offers or products based on recipient preferences.
- Optimize Email Copy:
- Write clear, concise, and benefit-focused copy that highlights value (e.g., “Discover How to Save Time with Our Tool”).
- Use action-oriented language in CTAs (e.g., “Shop Now” or “Claim Your Discount”).
- Break up text with bullet points or short paragraphs for readability.
- Design Clear and Prominent CTAs:
- Use visually distinct buttons for CTAs with contrasting colors and clear text (e.g., “Get Started”).
- Place CTAs strategically, such as above the fold and repeated in longer emails.
- Limit to one primary CTA to avoid overwhelming the reader.
- Segment Your Audience:
- Divide your email list into segments based on demographics, behavior, or engagement level (e.g., active vs. inactive users).
- Send targeted content to each segment to increase relevance and clicks (e.g., special offers for loyal customers).
- Optimize for Mobile:
- Ensure emails are mobile-responsive, as over 50% of emails are opened on mobile devices.
- Use single-column layouts, large fonts (14-16px), and touch-friendly CTA buttons (at least 44×44 pixels).
48. Define The Following Metrics:- Open Rate, Click Through Rate, Response Rate, and Forward Rate?
It is one of the most common Interview questions for digital marketing that is often asked during the interview sessions. So, you need to be well prepared for it.
- Open Rate: Reflects the effectiveness of subject lines and sender reputation. Accuracy may be affected by email clients blocking tracking pixels (e.g., Apple’s Mail Privacy Protection).
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Measures how engaging your email content and calls-to-action are, indicating user interest in your links or offers.
- Response Rate: Depends on the campaign’s goal (e.g., replies for B2B, form submissions for lead generation). It’s less commonly tracked but valuable for interactive campaigns.
- Forward Rate: Shows how shareable your email is, reflecting brand advocacy. Tracking may require specific features in email service providers (e.g., Mailchimp, HubSpot).
49. How To Recapture Inactive Customers?
Recapturing inactive customers involves re-engaging users who haven’t interacted with your brand recently (e.g., no opens, clicks, or purchases in a defined period, typically 3-6 months). Based on email marketing and customer retention best practices, here are actionable strategies to win back inactive customers:
1. Identify and Segment Inactive Customers
- Define Inactivity: Use your CRM or email service provider (ESP) like Mailchimp or HubSpot to identify users who haven’t engaged (e.g., no email opens, clicks, or purchases) in a set timeframe.
- Segment the List: Group inactive customers by behavior (e.g., abandoned carts, lapsed buyers, or non-openers) to tailor re-engagement campaigns.
2. Craft a Re-Engagement Email Campaign
- Personalized Subject Lines: Use compelling, personalized subject lines like “We Miss You, [Name]!” or “Come Back for 20% Off Your Next Order.”
- Acknowledge Inactivity: Be transparent (e.g., “It’s been a while since we’ve seen you!”) to reconnect emotionally.
- Offer Incentives: Provide exclusive discounts, free shipping, or loyalty rewards to entice action. Example: “Get 25% Off to Welcome You Back!”
- Clear CTA: Include a prominent call-to-action (e.g., “Shop Now” or “Reactivate Your Account”) to drive engagement.
3. Use Urgency and Scarcity
- Create time-sensitive offers (e.g., “This 30% Off Expires in 48 Hours!”) to prompt immediate action.
- Highlight limited stock or exclusive deals to increase appeal.
4. Personalize Content
- Leverage past purchase or browsing data to recommend relevant products or services.
- Example: For an e-commerce store, show items related to their last purchase or items left in their cart.
5. Optimize for Mobile
- Ensure emails and landing pages are mobile-friendly, as many users check emails on their phones.
- Use responsive designs, large fonts, and touch-friendly CTA buttons.
50. What Are The Different Ways To Segment Buyer Personas?
Segmenting buyer personas involves dividing your audience into distinct groups based on shared characteristics to tailor marketing strategies effectively. It is one of the crucial interview questions for digital marketing that you must be well aware of. Here are the primary ways to segment buyer personas, based on marketing best practices:
1. Demographic Segmentation
- Definition: Grouping based on demographic traits.
- Examples: Age, gender, income level, education, occupation, marital status, or family size.
- Use Case: Targeting specific age groups (e.g., millennials vs. Gen Z) with tailored messaging, like promoting tech gadgets to younger audiences.
2. Geographic Segmentation
- Definition: Dividing based on location.
- Examples: Country, region, city, climate, or urban vs. rural areas.
- Use Case: Customizing offers based on location, such as promoting winter gear in colder regions or local events in specific cities.
3. Behavioral Segmentation
- Definition: Grouping based on user actions and interactions with your brand.
- Examples: Purchase history, website browsing behavior, email open/click rates, product usage frequency, or abandoned cart activity.
- Use Case: Sending re-engagement emails to inactive users or upselling related products to frequent buyers.
4. Psychographic Segmentation
- Definition: Segmenting based on lifestyle, values, interests, or personality traits.
- Examples: Hobbies, values (e.g., eco-conscious), attitudes, or lifestyle preferences (e.g., luxury vs. budget-conscious).
- Use Case: Targeting environmentally conscious consumers with sustainable products or appealing to adventure-seekers with travel gear.
5. Needs-Based Segmentation
- Definition: Grouping based on specific needs or pain points.
- Examples: Desire for convenience, cost savings, quality, or specific solutions (e.g., time-saving tools for busy professionals).
- Use Case: Offering premium support plans to customers who prioritize reliability.
6. Value-Based Segmentation
- Definition: Dividing based on the customer’s value to your business.
- Examples: High-value customers (e.g., frequent buyers), low-value customers, or one-time purchasers.
- Use Case: Offering exclusive loyalty rewards to high-value customers to retain them.
Final Takeaway
Hence, these are some of the crucial interview questions for digital marketing that you must be well aware of. Additionally, you can make use of these questions to crack your digital marketing interview in 2025.
You can share your views and comments in our comment box as it can help your business to grow in the right direction. If you want to crack your interview then you must be well aware of these facts as well.
- Ultimate Guide To Google Ads Optimization - October 17, 2025
- LinkedIn Profile Optimization: A Simple Guide - October 10, 2025
- How To Boost Your Followers On Instagram: 30 Simple Strategies - September 26, 2025


